Cache Strategies
tl;dr
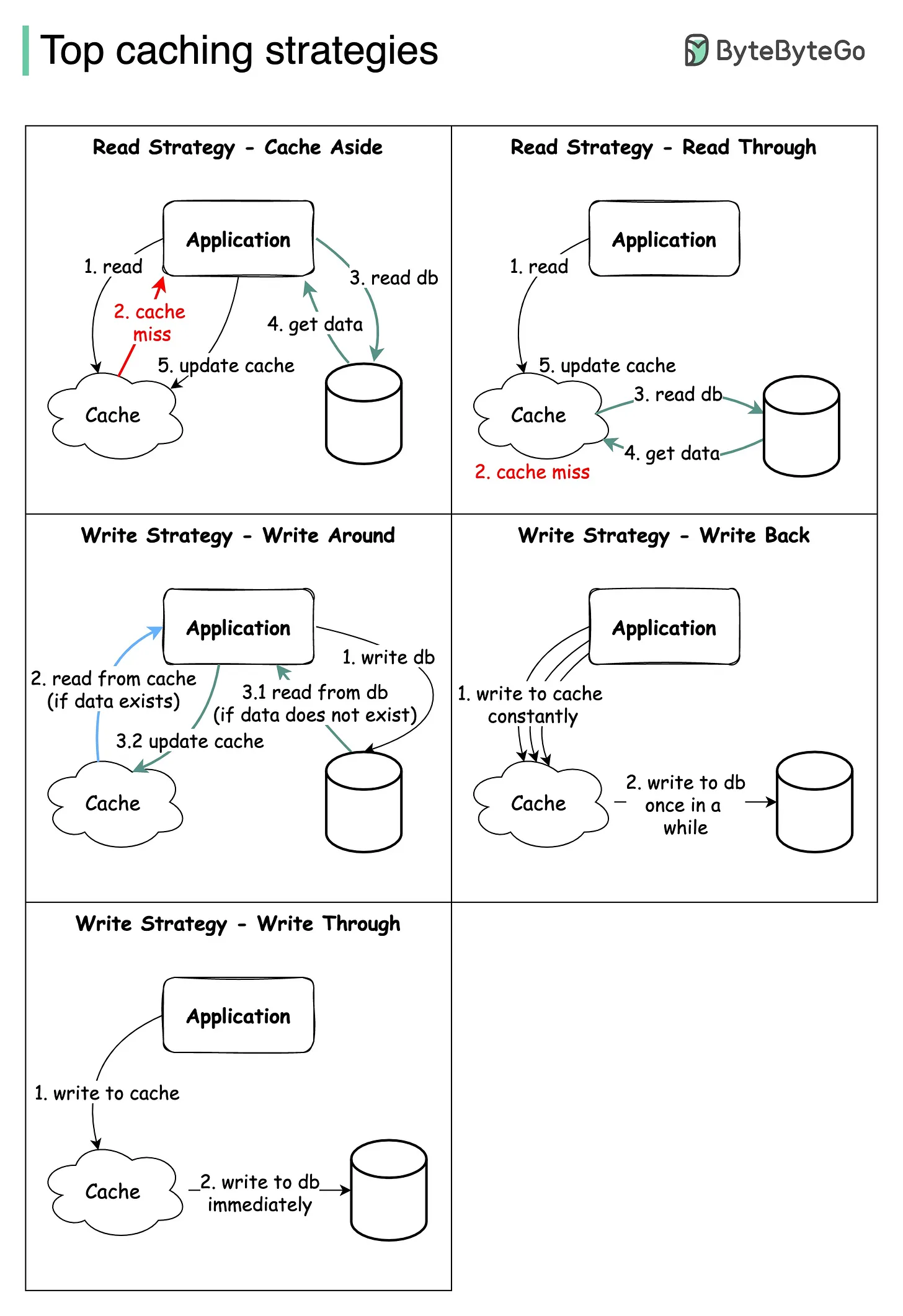
The diagram below illustrates how those 5 strategies work. Some of the caching strategies can be used together.
Read strategies
Read Cache Aside
The cache sits on the side, and the application directly talks to both the cache and the database.
There is no connection between the cache and the primary database. All operations to cache and the database are handled by the application.

Advantages
- Cache-aside caches are usually general purpose and work best for read-heavy workloads
- The read aside cache method can lead to faster performance and reduced response times as data is retrieved from the cache instead of the database or storage.
- It can result in reduced resource usage on the database or storage system.
Disadvantages
- Systems using cache-aside are resilient to cache failures. If the cache cluster goes down, the system can still operate by going directly to the database. (Although, it doesn’t help much if cache goes down during peak load. Response times can become terrible and in worst case, the database can stop working.)
When cache-aside is used, the most common write strategy is to write data to the database directly. When this happens, cache may become inconsistent with the database To deal with this, developers generally use time to live (TTL) and continue serving stale data until TTL expires. If data freshness must be guaranteed, developers either invalidate the cache entry or use an appropriate write strategy
Read Through
Read-through caches work best for write-heavy workloads workloads
Read-through cache sits in-line with the database.
When there is a cache miss, it loads missing data from database, populates the cache and returns it to the application.

Advantage
- logic for read-throw is usually supported by the library or stand-alone cache provider.
- The read-throw method ensures that the data being used is always up-to-date and accurate
Disadvantages
- when the data is requested the first time, it always miss cache and incurs the extra penalty of loading data to the cache.
- It can result in increased resource usage on the database or storage system.
Write strategies
Write Through
write-through caches work best for write-heavy workloads workloads
Data will write to the cache first and the cache immediately writes to the database
when recipt a data The data will be cached
Cache will send a request to save data to the database immediately.

Advantages
- There is never a cache miss, because data is always cached before being saved to the database.
- There is no case where the data does not match the database
- The data is always identical if we combine Write through cache and Read through cache.
Disadvantages
- The process of saving data will often take a extra time because it has to wait for the cache and database to be saved
- Most of the data on the cache is read-once data, so writing to the cache will result in a lot of unnecessary data remaining on the cache => unnecessary resource consumption
Write Back
Cache will synchronize data to the database periodically over time, or according to the amount of data inserted / updated.

Advantages
- Reduce the writing pressure on the database, thereby reducing costs and problems related to the database
- If we combine Write back and Read through cache, we have a good system for both read heavy workloads and write heavy workloads.
Disadvantages
- Data may not be consistent between the cache and the database if the cache has not synchronized the data to the database.
- If the cache is dead, the system will be dead, we may lose forever data that the cache has not synchronized to the database.
Write Around
This strategy is only suitable for data that rarely changes and the system accepts the delay of data, because data may not be consistent in the cache when the cache has not expired (expired) but has new data updated.

Advantages This strategy when there is data to change, will only be recorded in dB and skip the cache.
This will be able to reduce the cache that is flooded with record operations that it is likely that these data will never be used.
Disadvantages It is very easy to cause the case of "cache miss" if the client sends a new request from a new record, it will cause a delay when reading because the data must be read from the dB, then it is recorded in the cache and returns to the client.
Related Posts
Find more posts like this one.

January 10, 2024
I'm Done Typing npm
Are you tired of typing npm?
Read more
May 29, 2025
Load balancer RPC endpoints
Did your Dapp cash because of RPC endpoint?
Read more
May 15, 2025
Solidity: Storage Slots of Complex Types
This article explains how Solidity stores smart contract data using storage slots, packing for efficiency, and Yul assembly for direct storage access
Read more
May 13, 2025
Solidity: Storage Slots of Primary Types
This article explains how Solidity stores smart contract data using storage slots, packing for efficiency, and Yul assembly for direct storage access
Read more
May 9, 2025
Load Balancer
A load balancer is a device that distributes network traffic between multiple servers
Read more
May 9, 2025
Rate Limiting
Rate limiting is a technique used to control the rate of requests to a service.
Read more
May 13, 2025
Redis
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data structure store used as a database, cache, and message broker.
Read more
May 19, 2025
Javascript: deep cloning object methods
Read more
May 7, 2025
Prettier merged type
Prettier merged type
Read more
January 5, 2025
Should we use type or interface in typescript
Read more