Load Balancer

Load balancing is a technique used to distribute network traffic across a pool of servers. It optimizes network performance, reliability and capacity, reducing latency as the demand is equally distributed among multiple servers and compute resources.
How Load Balancing Works
- Load balancing sit between the servers and the internet.
- handle incoming requests from users for information.
- Once a request is received, the load balancer first determines which server in a pool is available and online and then routes the request to that server.
- during times of heavy loads, a load balancer acts promptly and can dynamically add servers in response to spikes in traffic. conversely, load balancers can drop servers if demand is low.
Benefits
-
Improved scalability.
- Load balancers can scale the server infrastructure on demand, depending on the network requirements, without affecting services.
- For example, if a website starts attracting a large number of visitors, it can cause a sudden spike in traffic. If the web server isn't able to manage this sudden influx of traffic, the website might crash. Load balancing can spread the extra traffic across multiple servers, preventing this from happening.
-
Improved efficiency.
- Due to the reduced burden of traffic on each server, the network traffic flows better and improves response times => This ultimately provides a better experience for site visitors.
-
Reduced downtime.
- Companies with a global presence and multiple locations in different time zones can benefit from load balancing, especially when it comes to server maintenance.
- For example, a company can shut down the server that needs maintenance and route traffic to the other available load balancers without causing service interruptions or downtime.
-
Predictive analysis
- Load balancing can provide early detection of failures and help manage them without affecting other resources.
- For example, software-based load balancers can predict traffic bottlenecks before they happen.
-
Efficient failure management
- In the event of a failure, load balancers can automatically redirect traffic to functional resources and backup options.
- For example, if a failure is detected on a network resource, such as a mail server, load balancers can redistribute resources to other unaffected areas to prevent service disruption.
-
Improved security
- Load balancers add an extra layer of security without requiring additional changes or resources.
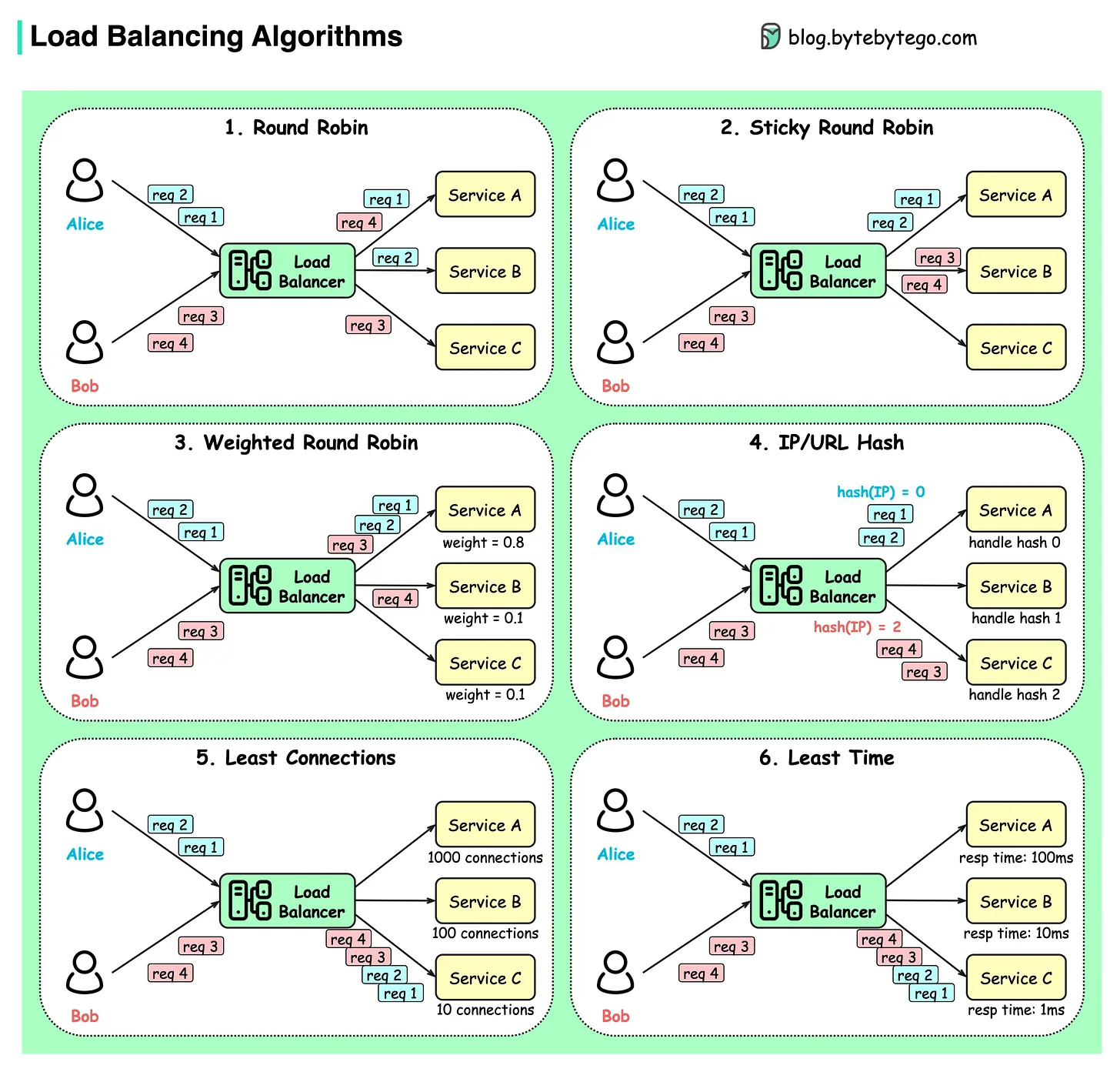
Algorithms
I found this blog explain the algorithms in a very detailed way: samwho/. i can't recommend it enough.
Related Posts
Find more posts like this one.

January 10, 2024
I'm Done Typing npm
Are you tired of typing npm?
Read more
May 29, 2025
Load balancer RPC endpoints
Did your Dapp cash because of RPC endpoint?
Read more
May 15, 2025
Solidity: Storage Slots of Complex Types
This article explains how Solidity stores smart contract data using storage slots, packing for efficiency, and Yul assembly for direct storage access
Read more
May 13, 2025
Solidity: Storage Slots of Primary Types
This article explains how Solidity stores smart contract data using storage slots, packing for efficiency, and Yul assembly for direct storage access
Read more
May 13, 2025
Cache Strategies
Cache strategies are a way to improve the performance of a system.
Read more
May 9, 2025
Rate Limiting
Rate limiting is a technique used to control the rate of requests to a service.
Read more
May 13, 2025
Redis
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data structure store used as a database, cache, and message broker.
Read more
May 19, 2025
Javascript: deep cloning object methods
Read more
May 7, 2025
Prettier merged type
Prettier merged type
Read more
January 5, 2025
Should we use type or interface in typescript
Read more